The Future of Aquaculture: Feeding the World Sustainably
Aquaculture, also known as fish farming, is the practice of raising fish, shellfish, and other aquatic animals in controlled environments like ponds, tanks, or cages in the ocean. It has been around for thousands of years, but recently, aquaculture has become one of the fastest-growing food-producing industries in the world.
With the global population expected to reach nearly 10 billion by 2050, traditional ways of fishing will not be enough to meet everyone’s seafood needs. Many fish stocks in oceans and rivers are already overfished, meaning these populations are shrinking and struggling to recover. Aquaculture could be the solution that helps feed the world sustainably. Here’s a look at the potential future of aquaculture and why it’s so important.
Why Aquaculture Is Important
Seafood is a key source of protein, vitamins, and minerals for billions of people worldwide. However, overfishing has caused major concerns for ecosystems and biodiversity in oceans and rivers. Aquaculture offers a way to provide seafood without further damaging natural fish populations.
In addition to feeding people, aquaculture has economic benefits. It creates millions of jobs for farmers, workers, and businesses all around the world. Many developing countries rely on aquaculture as a source of income and food security, so improving and expanding this industry could lift entire communities out of poverty.
Innovations Shaping the Future of Aquaculture
Aquaculture is evolving quickly thanks to modern technology, science, and environmental concerns. Here are some exciting advancements that are likely to shape the future of aquaculture:
1. Eco-Friendly Fish Farming
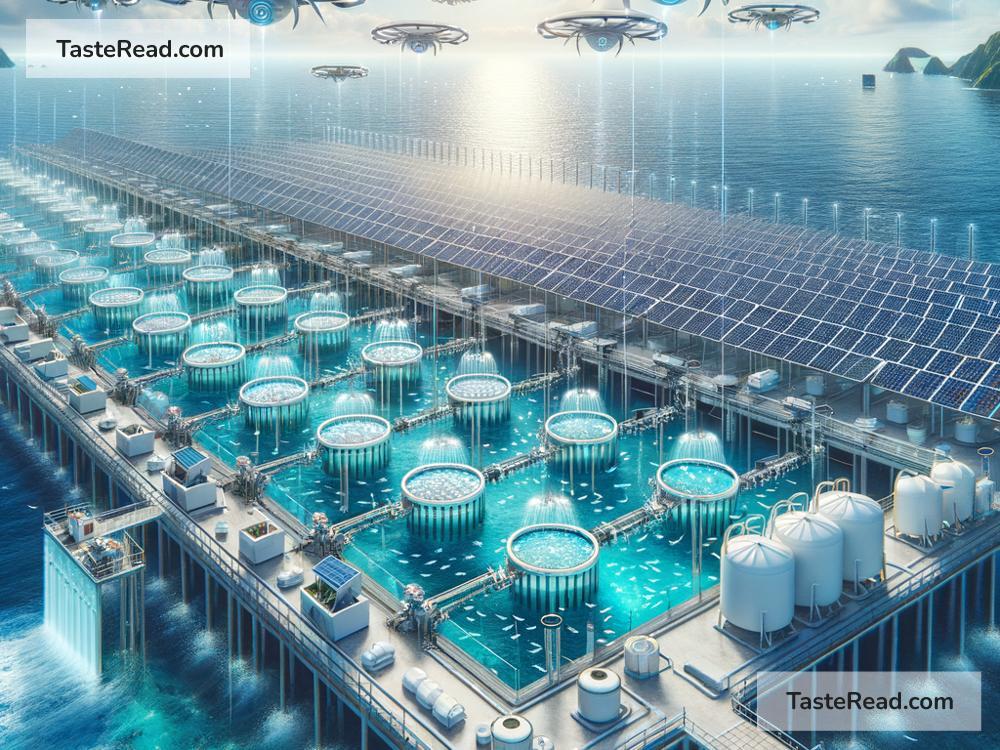
In the past, aquaculture has been criticized for polluting water and using up too many resources. But new technologies are helping farms become cleaner. For example, some farms use “recirculating systems,” which recycle water to reduce waste and prevent pollution. Others are turning to plant-based feeds for fish to reduce demand for wild fish used in traditional feed.
2. Offshore Farms
Instead of building fish farms near the shore, researchers and companies are exploring the idea of moving farms farther out into the ocean, where there is more space and less pollution. Offshore farms can give fish more room to grow and reduce environmental problems for coastal areas.
3. Integrated Systems
Many farms are beginning to combine different types of aquaculture and agriculture in one system. For instance, a farm might raise fish alongside seaweed and shellfish. The waste from the fish provides nutrients for the seaweed, and the seaweed filters the water to keep it clean. This creates a balanced and sustainable environment.
4. Using AI and Technology
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and automation are becoming major players in aquaculture. Farmers can now use computer systems to monitor water quality, feed fish automatically, and track growth. This saves time, reduces errors, and ensures fish have the best possible conditions.
5. Breeding and Genetics
Scientists are working on selecting and breeding fish that grow faster, resist diseases, and have better nutrition. This doesn’t involve genetic modification but rather choosing the strongest and healthiest fish to create future generations. This makes farming more efficient and helps meet the growing demand for seafood.
Challenges for the Future of Aquaculture
Despite its potential, aquaculture still faces many challenges that need to be overcome for it to grow responsibly. One of the biggest concerns is environmental impact. If not managed properly, fish farms can pollute water, harm local wildlife, and spoil ecosystems.
Diseases and pests are another big issue. When many fish live in small spaces, they are more likely to get sick, and these diseases can spread to wild populations. Farmers are working hard to find smarter, eco-friendly ways to prevent and treat diseases.
Finally, there are social and economic challenges. Aquaculture can be expensive to start and requires access to modern technologies, which might not be available in poorer countries. To solve this, governments, researchers, and organizations will need to work together to make aquaculture affordable and accessible for everyone who wants to try it.
Sustainability: The Key to Success
If aquaculture is to be part of the solution to food insecurity, it must focus on sustainability. This means finding ways to farm seafood that don’t harm the planet or deplete resources. Many farms are working toward this by using green energy, reducing waste, and improving water management.
Seaweed farming is an exciting part of aquaculture’s sustainable future. Seaweed grows without fertilizer or freshwater, absorbs carbon dioxide, and provides a habitat for fish. It’s also nutritious and can be used in both human food and animal feed. Combining fish farming with seaweed farming could help solve many environmental challenges.
The Bigger Picture
The future of aquaculture looks promising, but it’s just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to feeding the world. Experts believe that aquaculture needs to work alongside other sustainable farming methods and fishing practices to ensure a stable food supply for future generations.
If done responsibly, aquaculture can help reduce pressure on wild fish populations, provide healthier food options, and create economic opportunities for communities around the world. By focusing on innovation, sustainability, and collaboration, aquaculture can play a major role in tackling hunger and protecting our planet.
In conclusion, aquaculture’s future is bright, but it requires smart decisions and careful planning. With new technology, creativity, and teamwork, fish farming can grow into an industry that helps feed billions while protecting the earth’s ecosystems.